Table Of Content

The Observer pattern is a powerful design pattern that allows objects to communicate with each other in a loosely coupled way. By using this pattern, you can create flexible, modular, and reusable code that is easy to maintain and extend. Usually, the order in which observers are updated is not deterministic and is up to the subject's decision. You should, therefore, avoid any logic that depends on a specific order in which the observers receive their update call, as this may likely change. Since you don't know which observers will eventually register at the subject, there is also no easy way to enforce any rules here. The best way to avoid these issues is to group related updates into a transaction and ensure that the notification is only fired after the transaction is completed successfully.
Some other Popular Design Patterns
The "push" model compromises reuse, while the "pull" model isless efficient. Rollison advised businesses relying on TikTok to make contingency plans in event of a ban, sticking with short-form video, given the appetite for such content. “Everybody who’s involved in deciding whether or not this platform is going to get banned is turning a blind eye to how it’s going to affect all of the small businesses,” said Bilal Rehman of Texas. This novel approach suggested more similarity between parents and offspring – approximately 40% rather than the 25% of previous studies.
New York City C-PACE Program Remains in Holding Pattern - Commercial Observer
New York City C-PACE Program Remains in Holding Pattern.
Posted: Tue, 11 Apr 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Observer Design Pattern in Java
In this example, the Observer pattern lets the text editor object notify other service objects about changes in its state. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the Observer pattern and illustrate its functionality, we will implement a straightforward chat application using Python. This allows the number and "type" of "view" objects to be configureddynamically, instead of being statically specified at compile-time. You can reduce this problem by ensuring that updates are only fired and handled if the state really changes. However, the problem is best fixed by redesigning your UI and backend to avoid redundant updates. Well, it actually is...there are only a few details we have to look at regarding the updates between subject and observer - as there are different strategies for that.
Step Wise Implementation of above Problem:
The study concluded that it was “impossible to accurately predict a child’s personality traits from those of their mother or father” and that most relatives are not “much more similar than strangers”. Please note that the usage is very raw, and the tutorial is about Observer not Flows or Coroutines as they’re a vast topic, you should research if you haven’t used them before. Depending on used Flow there might be a single collector or multiple collectors. It might emit the last cached value or only when something changes.
ConcreteSubject
Yet, the update should only be fired after all changes are processed. Think of someone updating different address fields like street, number, or city name. While you could fire an update every time one of these fields changes, this would result in some observers showing inconsistent data, like a wrong number of a street not present in the given city.
Use Cases of Observer Method Design Pattern
The Observer Pattern helps decouple the weather monitoring system from the components interested in weather updates. Each component can register as an observer, and when the weather changes, the observers are notified. This way, adding or removing components doesn’t affect the weather monitoring system.
Step 4: How to notify the Subscribe Customers?
You must notify the client about the store equipment each time products change. Chain of Responsibility passes requests along a chain of potential receivers, while the Observer pattern facilitates subscription-based notifications. This approach resembles a notification system, informing various listeners about specific events. Subject represents the core (or independent or common or engine)abstraction. Observer represents the variable (or dependent oroptional or user interface) abstraction. One small correction, after notifyObservers();, you should nullify this.message, so that getUpdate should be returned null.
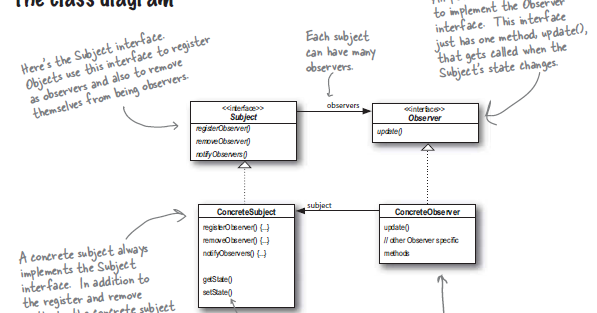
The observers then need to ask for the changed status by means of a separate method request. Besides other well-known patterns such as the visitor pattern or the singleton pattern, the observer pattern belongs to this collection of practical design patterns. We explain what the observer design pattern can do, present it in a UML diagram, and cover the strengths and weaknesses of the pattern. In this UML class diagram, the Subject class does not update the state of dependent objects directly. Instead, Subject refers to the Observer interface (update()) for updating state, which makes the Subject independent of how the state of dependent objects is updated. The Observer1 and Observer2 classes implement the Observer interface by synchronizing their state with subject's state.
The same can happen if your subject is a derived class and its base class manages the update handling. Calling the base's setter method could result in an update call before any logic from the derived class was called. Observer design pattern is useful when you are interested in the state of an object and want to get notified whenever there is any change. In observer pattern, the object that watch on the state of another object are called Observer and the object that is being watched is called Subject. As soon as the state of subject changes, subject notifies all the registered observers and the observers can access the updated state and act accordingly. Two different methods are available for informing the individual observers.
Whether the object we want to notify is an explorer window, a browser window, or even a printer doesn't matter as long as it has an update method we can call for sending our latest changes. In this example, a text published by the subject is displayed in the text fields of multiple observers. For this purpose, the subject class expands the observable class with the method addObserver(). Moreover, the method setChanged() is introduced which registers changes to the subject and, in the event of changes, invokes notifyObservers() to inform all observers. They hold the actual state or data that observers want to track. When this state changes, concrete subjects notify their observers.
Another problem with the observer design pattern is that in the source code of the subject, it is often not apparent which observers are to be supplied with information. They register with a concrete subject and react when notified of a state change. When the subject’s state changes, the concrete observer’s update() method is invoked, allowing it to take appropriate actions.

No comments:
Post a Comment